3.2 Operating principle of a heat pump
The heat pump consists of four main components:
- evaporator
- compressor
- condenser
- expansion valve.
The solar energy stored in the soil is collected by the brine circulating in the brine circuits. In the evaporator (4), energy contained in the heat collecting liquid is transferred to the refrigerant, which absorbs the heat energy as it evaporates. The heat collecting liquid returns to the ground approximately 3 °C cooler than when it came. The brine entering the heat pump can be no colder than –5 °C.
The pressure and temperature of the refrigerant increase in the compressor (3). The refrigerant also absorbs the heat energy created by the compressor’s work.
Hot gas is transferred into the condenser (2). The condenser transfers the heat energy from the refrigerant into the water circulating in the heating system, which distributes it to heat the building and the domestic water with the help of a change-over valve. The refrigerant condenses into a liquid state in the condenser as it loses heat energy.
The pressure of the refrigerant remains high as the liquid refrigerant is transferred to the expansion valve (6). The pressure of the refrigerant decreases in the expansion valve, and its temperature drops to approximately –10 °C. The expansion valve injects the correct amount of refrigerant into the evaporator, where the heat energy transferred from the brine causes the refrigerant to evaporate.
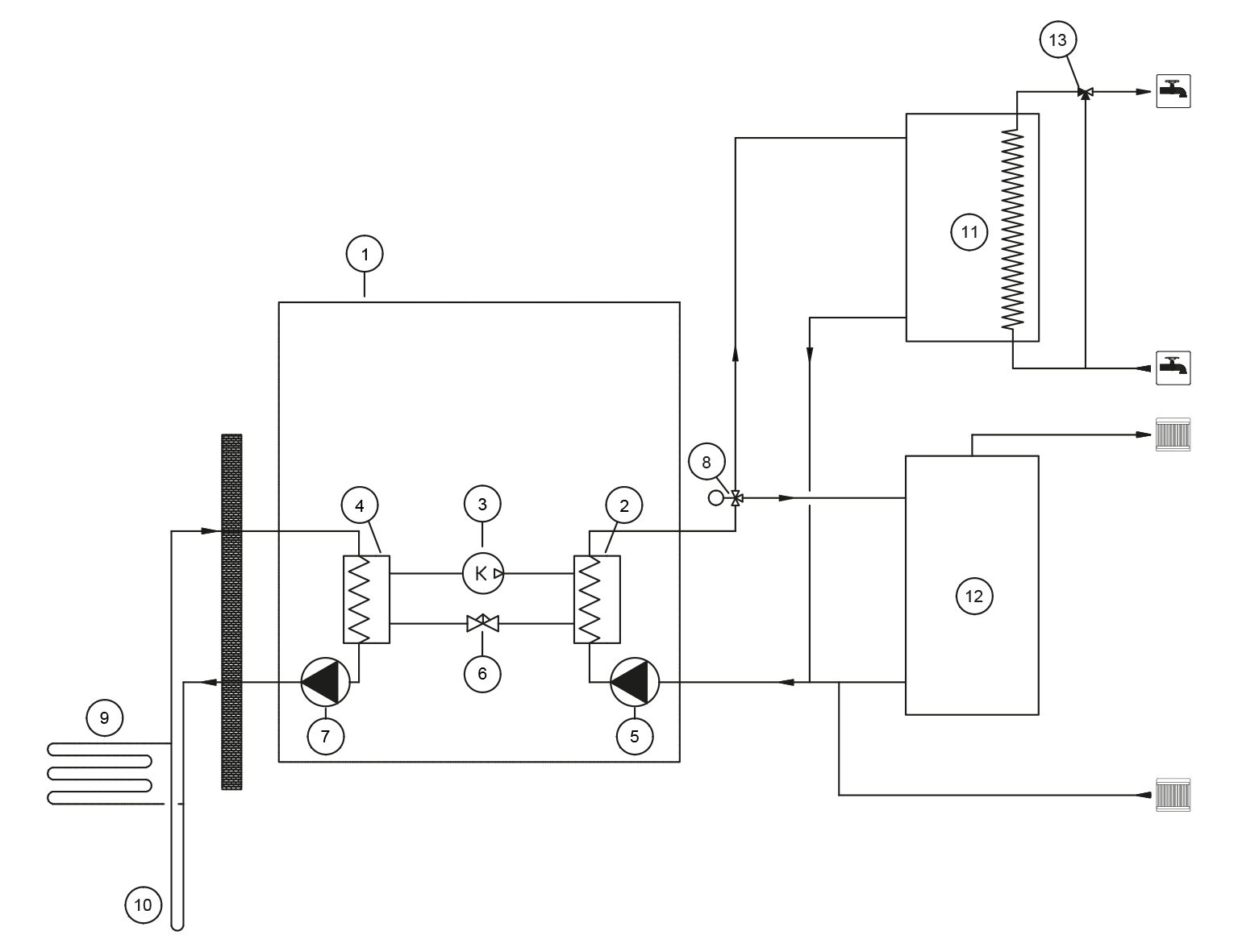
| 1 | Heat pump | 8 | Change-over valve |
| 2 | Condenser | 9 | Heat collection pipe, ground loop |
| 3 | Compressor | 10 | Heat collection pipe, bored well |
| 4 | Evaporator | 11 | Domestic water accumulator |
| 5 | Charge pump | 12 | Heating accumulator |
| 6 | Expansion valve | 13 | Domestic water control valve |
| 7 | Source pump |
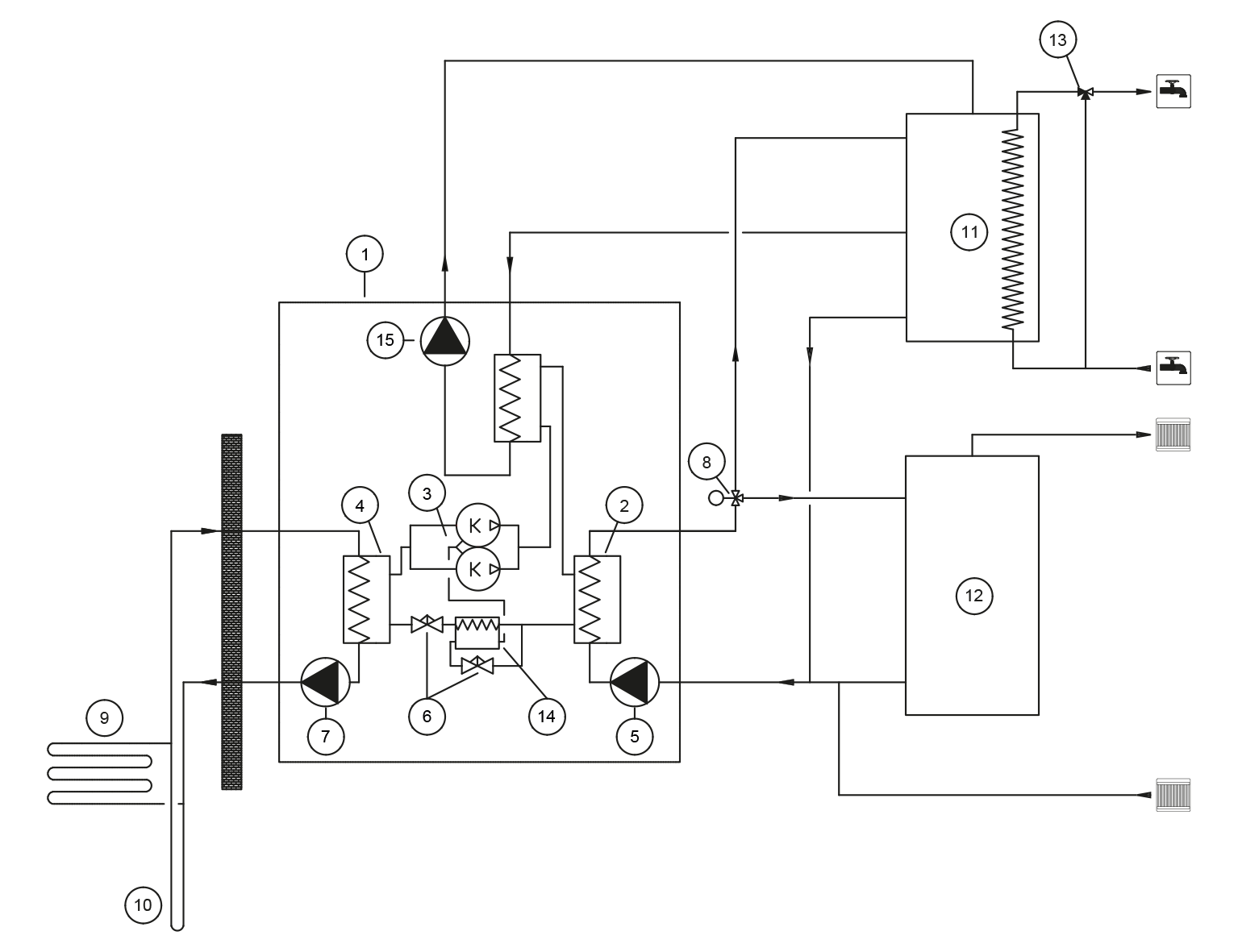
| 1 | Heat pump | 9 | Heat collection pipe, ground loop |
| 2 | Condenser | 10 | Heat collection pipe, bored well |
| 3 | Compressor | 11 | Domestic water accumulator |
| 4 | Evaporator | 12 | Heating accumulator |
| 5 | Charge pump | 13 | Domestic water control valve |
| 6 | Expansion valve | 14 | Economizer |
| 7 | Source pump | 15 | Superheating pump |
| 8 | Change-over valve |